 This is a real nice looking image.
This is a real nice looking image.
Abstract
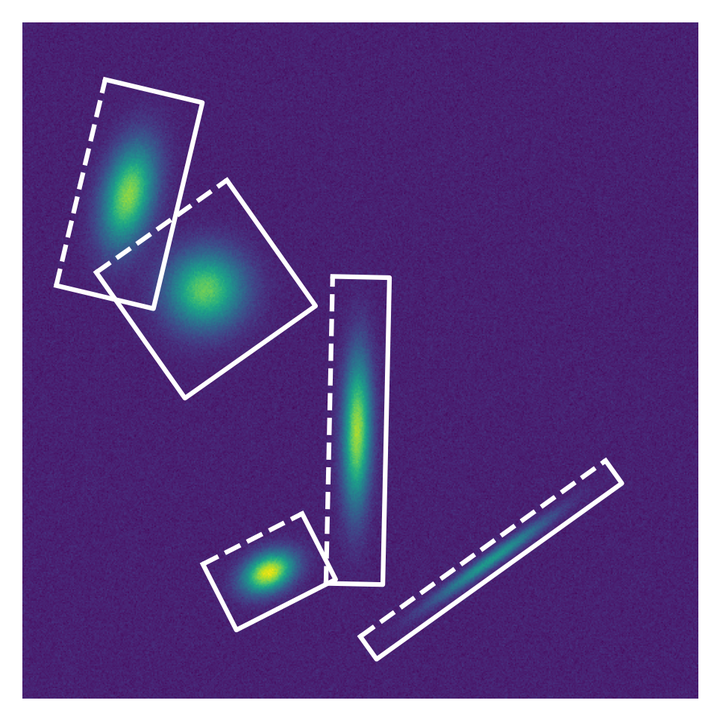
A deep neural network (NN) is used to simultaneously detect laser beams in images and measure their center coordinates, radii, and angular orientations. A dataset of images containing simulated laser beams and a dataset of images with experimental laser beams—generated using a spatial light modulator—are used to train and evaluate the NN. After training on the simulated dataset the NN achieves beam parameter root mean square errors (RMSEs) of less than 3.4% on the experimental dataset. Subsequent training on the experimental dataset causes the RMSEs to fall below 1.1%. The NN method can be used as a stand-alone measurement of the beam parameters or can compliment other beam profiling methods by providing an accurate region-of-interest.
Type
Publication
In Applied Optics